|
|
 |
Comparing CyberKnife radiosurgery to radiation therapies
Radiation therapy has been used for decades to treat prostate cancer with varying degrees of success. The goal of any radiation therapy for prostate cancer is to deliver the appropriate dose of radiation needed to treat the cancer, while protecting the surrounding tissues and structures, and minimizing patient discomfort and side effects.
Today, CyberKnife Robotic-assisted Radiosurgery - a robotic radiation therapy that sounds like surgery, but isn't - is offering new hope for patients with localized prostate cancer. It also can be used to treat prostate cancer that has recurred after a radical prostatectomy or previous treatment. CyberKnife has been used to treat prostate cancer for about six years. Studies are showing CyberKnife treatment produces exceptionally good PSA responses with a low incidence of side effects.
 Download the complete comparison of CyberKnife and Radiation Therapies Download the complete comparison of CyberKnife and Radiation Therapies
Treatment Preparation
| CyberKnife Radiosurgery |
Tiny gold markers (fiducials) implanted in a procedure similar to a biopsy |
| External Beam Radiotherapy(EBRT) |
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy(IMRT) |
Tiny gold markers (fiducials) may be implanted in a procedure similar to a biopsy |
| Calypso-Guided EEBRT/IMRT |
Very small Calypso beacons implanted in a procedure similar to a biopsy |
| High-Dose-Rate(HDR)Brachytherapy |
Ultrasound or CT scan performed to dermine the prostate size prior to treatment |
| Low-Dose-Rate(LDR)Brachytherapy(Seed Implant) |
Ultrasound probe placed in rectum to determine prostate size and shape for pre-implant radiation plan |
Length of Treatment
| |
Hospital Stay |
Number/Length of Treatments |
| CyberKnife Radiosurgery |
No hospital stay |
1 treatment daily for 5 days |
| External Beam Radiotherapy(EBRT) |
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy(IMRT) |
No hospital stay |
1 treatment daily for 8-9 weeks |
| Calypso-Guided EEBRT/IMRT |
No hospital stay |
1 treatment daily for 8-9 weeks |
| High-Dose-Rate(HDR)Brachytherapy |
One or two hospitals stays (1 to 2 days each) |
1- to 2-day hospital stay, plus 5 weeks of external beam radiation therapy; or two implants with 1- to 2-day hospital stay each |
| Low-Dose-Rate(LDR)Brachytherapy(Seed Implant) |
No hospital stay |
Single outpatient procedure; additional 5 weeks of external beam radiation therapy may be required |
Anesthesia
| CyberKnife Radiosurgery |
No anesthesia |
| External Beam Radiotherapy(EBRT) |
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy(IMRT) |
No anesthesia |
| Calypso-Guided EEBRT/IMRT |
No anesthesia |
| High-Dose-Rate(HDR)Brachytherapy |
Spinal or general anesthesia during needle/catheter placement |
| Low-Dose-Rate(LDR)Brachytherapy(Seed Implant) |
Spinal or general anesthesia during needle/seed implant |
Treatment Delivery
| |
Biologically equivalent radiation dose(*) |
Method of Radiation Delivery |
| CyberKnife Radiosurgery |
200 Gy |
Concentrates 150-200 beams of radiation on prostate from numerous angles and locations |
| External Beam Radiotherapy(EBRT) |
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy(IMRT) |
150-160 Gy |
Aims 5-7 beams of radiation at prostate from a single arc |
| Calypso-Guided EEBRT/IMRT |
150-160 Gy |
Aims 5-7 beams of radiation at prostate from a single arc |
| High-Dose-Rate(HDR)Brachytherapy |
170-220 Gy |
15-20 small tubes (catheters) are inserted into the prostate to be used to deliver radiation |
| Low-Dose-Rate(LDR)Brachytherapy(Seed Implant) |
170-210 Gy |
20 or more needles inserted into the prostate permanently deposit about 100 radioactive seeds, which then release radiation over a period of time |
(*)Biologically equivalent radiation dose: using linear-quadratic model to convert to a BED, assuming alpha/beta ratio of 2Gy.
Accuracy
| CyberKnife Radiosurgery |
One-millimeter accuracy protects surrounding tissues |
| External Beam Radiotherapy(EBRT) |
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy(IMRT) |
Target area is expanded to include the prostate plus 5-10 millimeters to account for uncertainty |
| Calypso-Guided EEBRT/IMRT |
Target area is expanded to include the prostate plus approximately 5 millimeters to account for uncertainty |
| High-Dose-Rate(HDR)Brachytherapy |
Custom radiation plan delivers radiation dose to within 2-3 millimeters of the target, which spares surrounding tissues |
| Low-Dose-Rate(LDR)Brachytherapy(Seed Implant) |
Seeds positioned with 3-5 millimeters accuracy; occasionally some seeds migrate to the lung(s) |
| |
Correcting for movement |
Method of targeting/tracking |
| CyberKnife Radiosurgery |
Throughout treatment robot automatically adjusts for any movement or rotation |
Robot autmotatically locates fiducials |
| External Beam Radiotherapy(EBRT) |
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy(IMRT) |
Technician manually adjusts prior to each treatment session; no real-time correction for any movement or rotation during treatment |
Patient's skin is marked and therapist aligns on those two marks, or targets fiducials using X-ray images |
| Calypso-Guided EEBRT/IMRT |
If movement exceeds error threshold (3 mm), treatment stops and technician manually adjusts treatment table; no correction for rotation |
Radio-frequency detector determines beacon location. Therapist manually adjusts treatment table accordingly |
| High-Dose-Rate(HDR)Brachytherapy |
Physician manually places catheters using ultrasound images for guidance; a customized treatment plan accounts for variation in catheter position |
Ultrasound probe placed in rectum visualizes prostate and needle/catheter position |
| Low-Dose-Rate(LDR)Brachytherapy(Seed Implant) |
Physician manually places needles using ultrasound images for guidance; no corrections possible after seeds have been implanted |
Ultrasound probe placed in rectum visualizes prostate and needle/seed position |
Side Effects
| |
Side effects during/after treatment |
| CyberKnife Radiosurgery |
Mild to moderate urinary problems and mild fatigue for 1-2 months; about 1% of patients need catheterization for urinary retention; resume normal activity immediately after treatment |
| External Beam Radiotherapy(EBRT) |
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy(IMRT) |
Mild urinary and bowel problems and mild fatigue for 2 months; need for catheterization for urinary retention is rare; resume normal activity immediately after treatment |
| Calypso-Guided EEBRT/IMRT |
Mild urinary and bowel problems and mild fatigue for 2 months; need for catheterization for urinary retention is rare; resume normal activity immediately after treatment |
| High-Dose-Rate(HDR)Brachytherapy |
Mild pain from catheters; moderate urinary problems and fatigue for 1-2 months; about 3% of patients need catheterization for urinary retention; resume normal activity 1-2 days after leaving the hospital |
| Low-Dose-Rate(LDR)Brachytherapy(Seed Implant) |
Pain at needle insertions; mild to severe urinary symptoms for 1-3 months; brief, mild fatigue; about 8% of patients need catheterization of urinary retention; resume normal activity day after implant |
| |
Long-term side effects |
| CyberKnife Radiosurgery |
Despite receiving a dose similar to brachytherapy, long-term urinary effects are not common and rectal injury is rare; 20-30% patients develop erectile dysfunction
|
| External Beam Radiotherapy(EBRT) |
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy(IMRT) |
Long-term urinary and rectal injury is not common; approximately 1/3 of patients develop erectile dysfunction |
| Calypso-Guided EEBRT/IMRT |
Long-term urinary and rectal injury is not common; approximately 1/3 of patients develop erectile dysfunction
|
| High-Dose-Rate(HDR)Brachytherapy |
Occasional long-term urinary effects; rectal injury is rare; approximately 1/3 of patients develop erectile dysfunction |
| Low-Dose-Rate(LDR)Brachytherapy(Seed Implant) |
Frequent long-term urinary effects; rectal injury is not common; approximately 1/3 of patients develop erectile dysfunction |
Outcomes (cancer-control rates/freedom from PSA rise)
| CyberKnife Radiosurgery |
PSA responses suggest long-term cancer control rates will be excellent (awaiting data from long-term studies) |
| External Beam Radiotherapy(EBRT) |
Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy(IMRT) |
10+ year cancer-control outcomes inferior to brachytherapy; increasing the dose using image-guidance may improve results |
| Calypso-Guided EEBRT/IMRT |
10+ year cancer-control outcomes inferior to brachytherapy; Calypso guidance may allow increase dose with improved results |
| High-Dose-Rate(HDR)Brachytherapy |
Excellent cancer-control rates with 5-10 year follow-up |
| Low-Dose-Rate(LDR)Brachytherapy(Seed Implant) |
Excellent cancer control rates with 10-15 year follow-up |
 Download the complete comparison of CyberKnife and Radiation Therapies. Download the complete comparison of CyberKnife and Radiation Therapies.
External Beam Radiotherapy (EBRT)
External Beam Radiotherapy (EBRT) has been used for decades to treat localized prostate cancer. EBRT delivers five to seven beams of radiation from a source outside the body. The accuracy and orientation of the beams of radiation are limited by the equipment. To compensate for patient and prostate movement and the inaccuracy of the EBRT equipment, the physician must target the prostate and a rim of surrounding normal tissue. This means portions of the nearby rectum and bladder receive a full dose of radiation. To prevent injury to these tissues, radiation is delivered in many small, daily doses over a period of eight to nine weeks.
Older EBRT techniques delivered 65-70 Gy (units of radiation), which is now considered inadequate. Modern advancements, such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and image-guidance radiotherapy (IGRT) have made it possible to increase external beam radiation doses. While these higher doses improved cancer control rates, they remained inferior to the cure rates with brachytherapy.
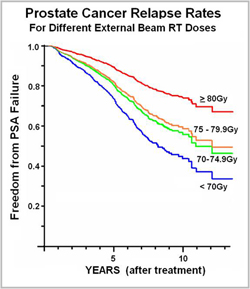 This graph shows the proportion of patients free from a recurrence of prostate cancer in the years following various doses of external beam radiotherapy. If an EBRT treatment is curative, the downward trend should level off and become a horizontal line (which corresponds with the cure rate). As shown, prostate cancer treated with a higher dose (80 Gy or greater) takes longer to recur, but there is no clear leveling off. This suggests even the highest doses of external beam radiotherapy may be insufficient to cure prostate cancer. (Data from Fox-Chase Cancer Center. Nadir+2 definition for biochemical failure used. Adapted from Eade IJROBP 68(3), 682-89.)
This graph shows the proportion of patients free from a recurrence of prostate cancer in the years following various doses of external beam radiotherapy. If an EBRT treatment is curative, the downward trend should level off and become a horizontal line (which corresponds with the cure rate). As shown, prostate cancer treated with a higher dose (80 Gy or greater) takes longer to recur, but there is no clear leveling off. This suggests even the highest doses of external beam radiotherapy may be insufficient to cure prostate cancer. (Data from Fox-Chase Cancer Center. Nadir+2 definition for biochemical failure used. Adapted from Eade IJROBP 68(3), 682-89.)
Low-Dose Rate Brachytherapy (seed implant)
Brachytherapy is a type of radiation therapy for prostate cancer. Unlike external beam radiation therapy that targets the cancer from a radiation source outside the body, with brachytherapy radiation is delivered from a source inside the body.
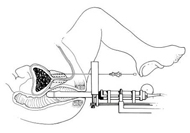 This is a side view of a LDR implant procedure. An ultrasound probe placed into the rectum guides needles into the prostate, where radioactive seeds” are deposited.
This is a side view of a LDR implant procedure. An ultrasound probe placed into the rectum guides needles into the prostate, where radioactive seeds” are deposited.
Over the next several weeks, the "seeds" slowly deliver radiation to the cancer. Eventually only non-radioactive "seeds" remain in the body.
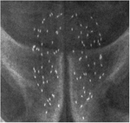 This X-ray shows the radioactive "seeds" throughout the prostate.
This X-ray shows the radioactive "seeds" throughout the prostate.
A higher dose of radiation can be delivered with seed implants than with external beam radiation. Cancer control rates are therefore higher with seed implants than with external beam radiation. Patients who have brachytherapy have cure rates similar to radical prostatectomy while avoiding major surgery.
Results have shown that with a sufficient dose of radiation, seed implants can cure prostate cancer. Patients who have brachytherapy have cure rates similar to radical prostatectomy while avoiding major surgery.
Advantages of LDR brachytherapy include:
- Treatment often requires only a single outpatient procedure
- Cure rates superior to external beam, and similar to radical prostatectomy
Disadvantages of LDR brachytherapy include:
- Required anesthesia
- Discomfort in the area where the needles were inserted for a few days after the procedure
- Temporary urinary discomfort and/or urgency following the procedure
- Urinary frequency and reduced stream, which may be permanent
- Urinary obstruction, which might require a catheter to drain the bladder
- Impotence rates five years after treatment are similar to radical prostatectomy
- Patients are radioactive for several weeks to months
High-Dose Rate Brachytherapy
High-dose rate brachytherapy is another method of giving internal radiation to the prostate.
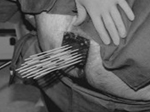 As with LDR implants, the patient is placed under general anesthesia or a spinal block that numbs the lower part of the body. An ultrasound probe is placed in the rectum, which guides the placement of 15-20 needles through the perineum (floor of the pelvis) into the prostate. The needles are then replaced with catheters which are held in place by a template that is sutured to the perineum. As with LDR implants, the patient is placed under general anesthesia or a spinal block that numbs the lower part of the body. An ultrasound probe is placed in the rectum, which guides the placement of 15-20 needles through the perineum (floor of the pelvis) into the prostate. The needles are then replaced with catheters which are held in place by a template that is sutured to the perineum.
After the catheters are in place, a CT scan determines the prostate location. A customized radiation plan is then developed for each patient. By adjusting the time the radiation source is programmed to be at each position in the catheters, the physician can compensate for possible errors in catheter positioning. The customized plan maximizes the radiation dose delivered to the prostate, while minimizing the dose to surrounding organs.
 A shielded after-loading device moves the high-intensity radiation source through the catheters into the prostate according to the plan. Radiation is then delivered to pre-programmed positions in the prostate in four to six large doses. This usually requires two separate implant procedures. A shielded after-loading device moves the high-intensity radiation source through the catheters into the prostate according to the plan. Radiation is then delivered to pre-programmed positions in the prostate in four to six large doses. This usually requires two separate implant procedures.
In most cancers, giving many small doses of radiation over a longer period of time helps avoid damage to normal tissues. In prostate cancer, however, prolonging treatment doesn't appear to offer any advantage over high doses of radiation delivered in a shorter period of time. Studies have shown that HDR brachytherapy alone (without additional external beam radiation therapy) has a five-year cancer relapse rate that is equal to or better than low-dose rate (LDR) brachytherapy (seed implant). Additionally, there are fewer acute and late side effects than with LDR brachytherapy. One study shows potency is also better preserved with HDR implants.
Advantages of HDR brachytherapy over LDR brachytherapy (seed implant) include:
- Fewer side effects after the catheters are removed
- Possible lower incidence of impotence
- Cure rates equal to or better than LDR implants
Disadvantages of HDR brachutherapy include:
- Patient must lie on his back in the hospital for one to two days with catheters in the prostate and a Foley catheter in the bladder
- Pain and discomfort while catheters are in place and also when they are removed without anesthesia
|
 |
|






 This graph shows the proportion of patients free from a recurrence of prostate cancer in the years following various doses of external beam radiotherapy. If an EBRT treatment is curative, the downward trend should level off and become a horizontal line (which corresponds with the cure rate). As shown, prostate cancer treated with a higher dose (80 Gy or greater) takes longer to recur, but there is no clear leveling off. This suggests even the highest doses of external beam radiotherapy may be insufficient to cure prostate cancer. (Data from Fox-Chase Cancer Center. Nadir+2 definition for biochemical failure used. Adapted from Eade IJROBP 68(3), 682-89.)
This graph shows the proportion of patients free from a recurrence of prostate cancer in the years following various doses of external beam radiotherapy. If an EBRT treatment is curative, the downward trend should level off and become a horizontal line (which corresponds with the cure rate). As shown, prostate cancer treated with a higher dose (80 Gy or greater) takes longer to recur, but there is no clear leveling off. This suggests even the highest doses of external beam radiotherapy may be insufficient to cure prostate cancer. (Data from Fox-Chase Cancer Center. Nadir+2 definition for biochemical failure used. Adapted from Eade IJROBP 68(3), 682-89.) This is a side view of a LDR implant procedure. An ultrasound probe placed into the rectum guides needles into the prostate, where radioactive seeds” are deposited.
This is a side view of a LDR implant procedure. An ultrasound probe placed into the rectum guides needles into the prostate, where radioactive seeds” are deposited.
 This X-ray shows the radioactive "seeds" throughout the prostate.
This X-ray shows the radioactive "seeds" throughout the prostate.
 As with LDR implants, the patient is placed under general anesthesia or a spinal block that numbs the lower part of the body. An ultrasound probe is placed in the rectum, which guides the placement of 15-20 needles through the perineum (floor of the pelvis) into the prostate. The needles are then replaced with catheters which are held in place by a template that is sutured to the perineum.
As with LDR implants, the patient is placed under general anesthesia or a spinal block that numbs the lower part of the body. An ultrasound probe is placed in the rectum, which guides the placement of 15-20 needles through the perineum (floor of the pelvis) into the prostate. The needles are then replaced with catheters which are held in place by a template that is sutured to the perineum.
 A shielded after-loading device moves the high-intensity radiation source through the catheters into the prostate according to the plan. Radiation is then delivered to pre-programmed positions in the prostate in four to six large doses. This usually requires two separate implant procedures.
A shielded after-loading device moves the high-intensity radiation source through the catheters into the prostate according to the plan. Radiation is then delivered to pre-programmed positions in the prostate in four to six large doses. This usually requires two separate implant procedures.
